Signals
A signal is the value of a particular measure of a circuit at a particular point over time.
Given Ohm's law, if current (I) is fixed and resistance (R) is dependent on the environment, then voltage (R) will give us a useful measure of, say, light levels or room temperature over time.
Analog
Electrical circuits produce (ideally) smooth analog signals that change their values continuously over time.

But computers don't work in analog, they are digital!
Signal Processing
We use hardware to convert continous analog signals to discrete digital signals that a computer can process.

These hardware enact a given protocol of signal processing to convert analog information into different forms of digital information, depending on the use case.
Binary
The basic building block of a computer is a transistor - invented at Bell labs in 1947 - which is either on or off, 1 or 0, determined by holding either a high or low voltage
By simply holding a binary (1/0) state, transistors can be built up into complex hardware configurations that can perform boolean operations, named after George Boole who developed them abstractly in the 19th century.
AND, OR and NOT are the logical building blocks of contemporary digital computation.
These are implemented in "gates", which are fixed circuits of transistors that perform these operations on electric charge, often registered in voltage (V).
Why do we care?
In order to take architecture online, we need to convert the analog physical world into a computable digital representation.
We will use the Arduino and the Johnny-Five framework to do so strictly in Javascript, originally a language for programming websites.
Arduino
"Arduino is an open-source electronics prototyping platform based on flexible, easy-to-use hardware and software. It's intended for artists, designers, hobbyists and anyone interested in creating interactive objects or environments."
-Arduino website
Johnny-Five
"Johnny-Five is an Open Source, JavaScript Arduino programming framework, developed at Bocoup."
-Johnny-Five README
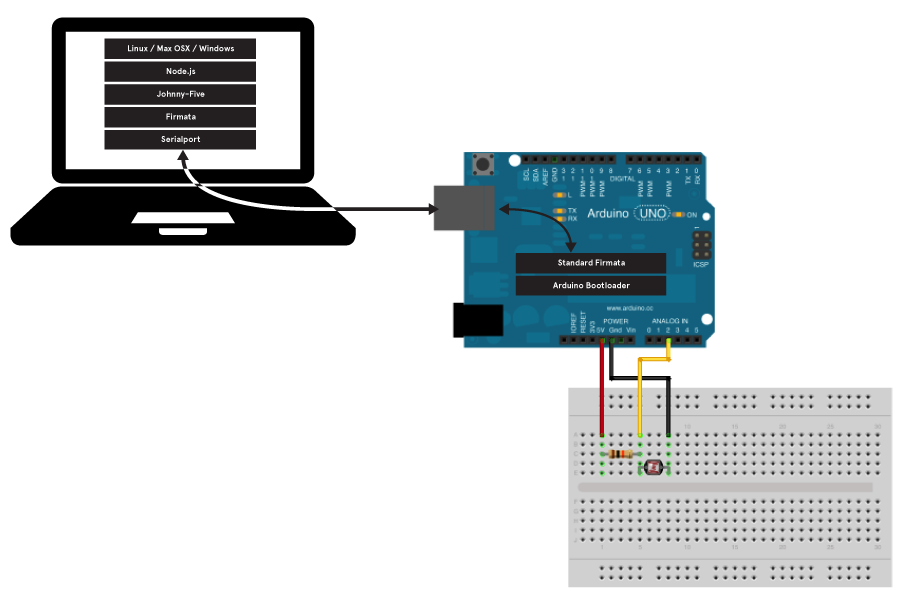
Johnny-Five builds on top of the serialport module and the firmata protocol to connect to and control an Arduino using only javascript in the Node.js embed environment.
{
"name": "johnny-five",
"description": "Firmata based Arduino Programming Framework.",
"version": "0.7.3",
"author": {
"name": "Rick Waldron <waldron.rick@gmail.com>",
"email": "waldron.rick@gmail.com"
},
"contributors": [
// MANY!!
],
"keywords": [
"arduino", "usb", "serial", "serialport", "firmata"
],
"licenses": [
{
"type": "MIT",
"url": "https://github.com/rwldrn/johnny-five/blob/master/LICENSE-MIT"
}
],
"engines": {
"node": ">=0.10.0"
},
"dependencies": {
"colors": ">=0.5.1",
"firmata": ">=0.2.9",
"lodash": ">=0.1.0",
"es6-collections": ">=0.0.1",
"socket.io": "latest",
"compulsive": "latest",
"temporal": "latest",
"descriptor": "latest",
"serialport": "latest",
"optimist": "~0.5.2",
"async": "~0.2.9",
"keypress": "latest"
}
}
An edited sample of the Johnny-Five package.json file.
Technology Stack 1.0
In our first iteration, we will use Johnny-Five to connect a laptop to the Arduino.

In our second iteration, we will use Johnny-Five read the inputs from a sensor through the Arduino to the laptop terminal.
Ultimately, we will swap out our laptops for a Raspberry Pi minicomputer.











